The global coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic lockdowns have caused global fossil carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions to decline by an estimated 2.4 billion tonnes or 7 percent in 2020 - a record drop according to researchers at the Global Carbon Project (GCP) and the UK's University of East Anglia (UEA), and the University of Exeter.
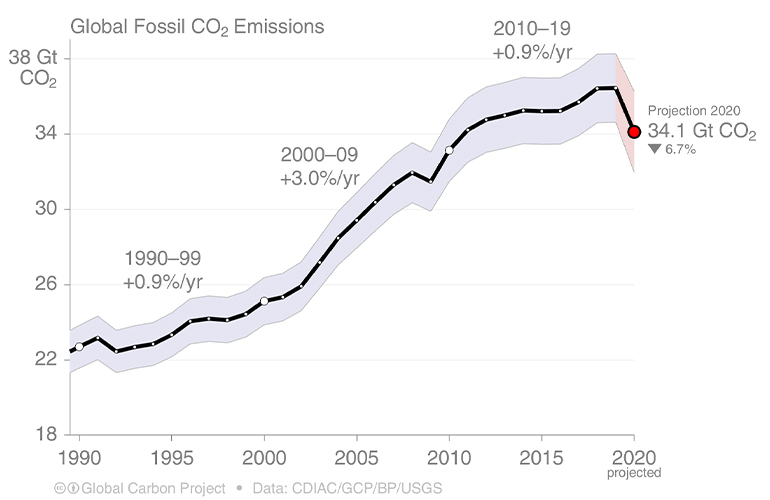
The decline is considerably larger than previous significant decreases – 0.5 (in 1981 and 2009), 0.7 (1992), and 0.9 (1945) billion tonnes of carbon dioxide (GtCO2). It means that in 2020 fossil CO2 emissions are predicted to be approximately 34 GtCO2, 7 percent lower than in 2019.
Emissions from transport account for the largest share of the global decrease. Those from surface transport, such as car journeys, fell by approximately half at the peak of the COVID lockdowns.
By December 2020, emissions from road transport and aviation were still below their 2019 levels, by approximately 10 percent and 40 percent, respectively, due to continuing restrictions.
Total anthropogenic CO2 emissions – from fossil CO2 and land-use change – are set to be around 39 GtCO2 in 2020.
Growth in CO2 emissions beginning to falter?
The release of Global Carbon Budget 2020, published on December 11, 2020, in the journal Earth System Science Data. coincides with the fifth anniversary of the adoption of the Paris Climate Agreement, which aims to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases (GHG) to limit global warming.
Cuts of around 1 to 2 GtCO2 are needed each year on average between 2020 and 2030 to limit climate change in line with its goals.
Five years on from the landmark agreement, the international team behind the annual carbon update says growth in global CO2 emissions had begun to falter, with emissions increasing more slowly in recent years, which could be partly in response to the spread of climate policy.
For the decade prior to 2020, fossil CO2 emissions decreased significantly in 24 countries while their economy continued to grow.
Regional differences
However, the researchers warn that it is too early to say how much emissions will rebound in 2021 and beyond, as the long-term trend in global fossil emissions will be largely influenced by actions to stimulate the global economy in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Professor Corinne Le Quéré, Royal Society Research Professor at UEA’s School of Environmental Sciences, contributed to this year’s analysis.
All elements are not yet in place for sustained decreases in global emission, and emissions are slowly edging back to 2019 levels. Government actions to stimulate the economy at the end of the COVID-19 pandemic can also help lower emissions and tackle climate change. Incentives that help accelerate the deployment of electric cars and renewable energy and support walking and cycling in cities are particularly timely given the extensive disturbance observed in the transport sector this year, said Professor Corinne Le Quéré.
The emissions decrease appears more pronounced in the United States (–12 percent) and EU27 countries (–11 percent), where COVID-19 restrictions accelerated previous reductions in emissions from coal use.

It appears least pronounced in China (–1.7 percent), where the effect of COVID-19 restrictions on emissions occurred on top of rising emissions. In addition, restrictions in China occurred early in the year and were more limited in their duration, giving the economy more time to recover.
In the UK, which first introduced lockdown measures in March 2020, emissions are projected to decrease by about 13 percent. The large decrease in UK emissions is due to the extensive lockdown restrictions and the second wave of the pandemic.
In India, where fossil CO2 emissions are projected to decrease about 9 percent, emissions were already lower than normal in late 2019 because of economic turmoil and strong hydropower generation, and the COVID-19 effect is potentially superimposed on this changing trend.
For the rest of the world, the effect of COVID-19 restrictions occurred on top of rising emissions, with emissions this year projected to decrease by about 7 percent.
Globally, the peak of the decrease in emissions in 2020 occurred in the first half of April, when lockdown measures were at their maximum, particularly across Europe and the United States.
Emissions from industry, for example, metal production, chemicals, and manufacturing reduced by up to a third during the COVID-19 lockdown in spring. However, they could already be back up to near or even above 2019 levels by now.

Despite lower emissions in 2020, the level of CO2 in the atmosphere continues to grow – by about 2.5 parts per million (ppm) in 2020 – and is projected to reach 412 ppm averaged over the year, 48 percent above pre-industrial levels.
Although global emissions were not as high as last year, they still amounted to about 39 billion tonnes of CO2, and inevitably led to a further increase in CO2 in the atmosphere. The atmospheric CO2 level, and consequently the world’s climate, will only stabilize when global CO2 emissions are near zero, said lead researcher Professor Pierre Friedlingstein, of the University of Exeter.
Fire, deforestation, and land-use change
Preliminary estimates based on fire emissions in deforestation areas indicate that net emissions from deforestation and other land-use change for 2020 are similar to the previous decade, at around 6 GtCO2.

Approximately 16 GtCO2 was released, primarily from deforestation, while the uptake of CO2 from regrowth on managed land, mainly after agricultural abandonment, was just under 11 GtCO2.
Measures to better manage land could both halt deforestation and help increase the CO2 sink from regrowth. Deforestation fires were lower this year compared to 2019 levels, which saw the highest rates of deforestation in the Amazon since 2008.
In 2019 deforestation and degradation fires were about 30 percent above the previous decade, while other tropical emissions, mainly from Indonesia, were twice as large as the previous decade because unusually dry conditions promoted peat burning and deforestation.

Land and ocean carbon sinks continue to increase in line with emissions, absorbing about 54 percent of the total human-induced emissions.
Facts
About Global Carbon Project
The Global Carbon Project (GCP) was established in 2001 by a shared partnership between the International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme (IGBP), the International Human Dimensions Programme on Global Environmental Change (IHDP), the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP) and Diversitas.
This partnership constituted the Earth Systems Science Partnership (ESSP) which subsequently evolved into Future Earth. The GCP is a Global Research Project of Future Earth and a research partner of the World Climate Research Programme.
It was formed to work with the international science community to establish a common and mutually agreed knowledge base to support policy debate and action to slow down and ultimately stop the increase of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere. The overwhelming realization that anthropogenic climate change is a reality has focused the attention of the scientific community, policymakers, and the general public on the rising atmospheric concentrations of the main GHGs – carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O).
The GCP has approached this challenge by focusing comprehensively on the global biogeochemical cycles which govern these three greenhouse gases, including their natural and human drivers, and opportunities for low carbon pathways.
Attempts through the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), first with its Kyoto Protocol and now with the Paris Agreement, are underway to stabilize the climate system which requires achieving a balance between sources and sinks of GHG.


